Yes, our doctors can treat an infected bug bite over telehealth. If antibiotics are needed to treat the infection, your telehealth doctor can send these prescriptions electronically to any pharmacy of your choice.
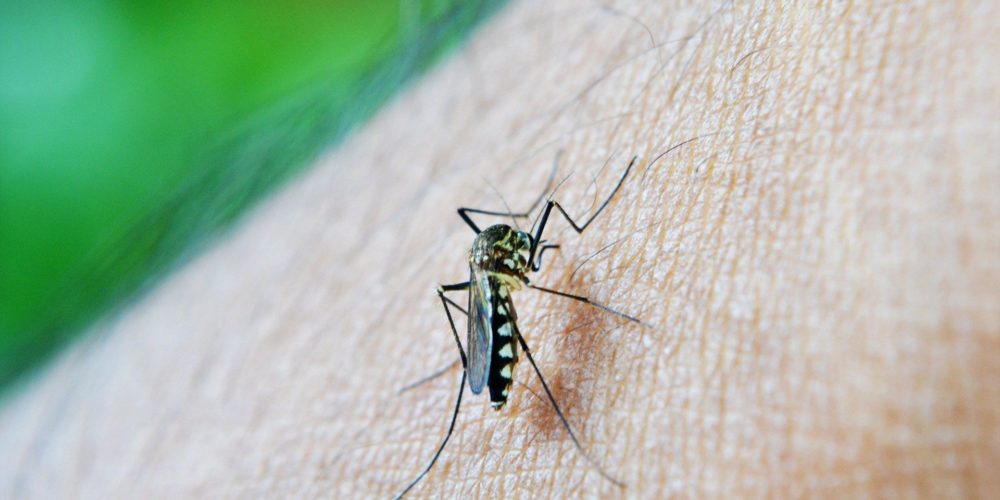
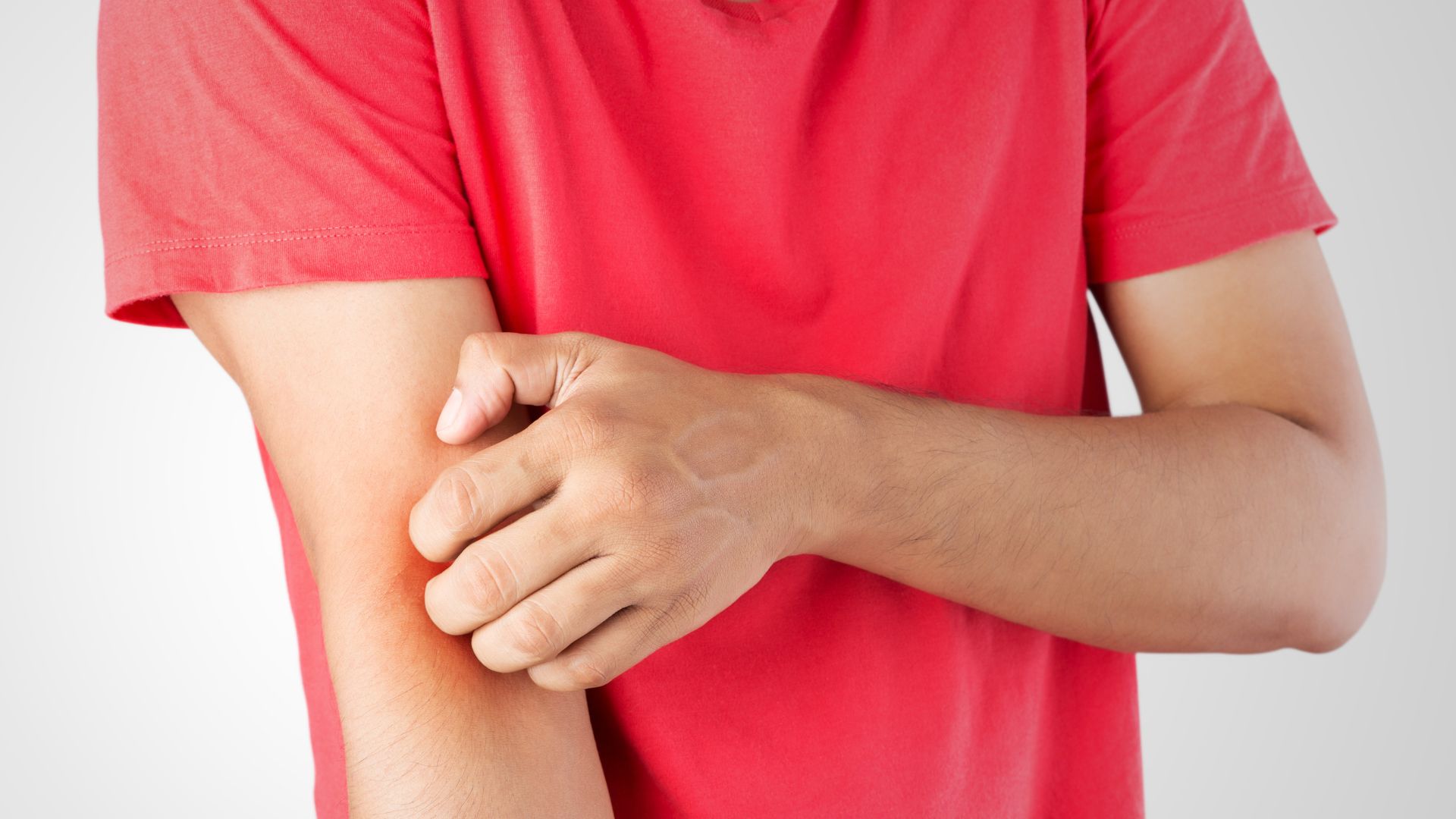
Insect bites are common and are often not a cause for concern. They might cause itching, swelling and stinging that will usually go away after a few days without the need for treatment. Some bites, however, can transmit disease-causing bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Stings from bees, yellow jackets, wasps, hornets, and fire ants might cause a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
The skin acts as a barrier to the harmless bacteria on its surface. If the skin breaks, these harmless bacteria can get under the skin and cause an infection.
An insect bite can penetrate the skin, allowing bacteria to enter. A common symptom of insect bites is a small, itchy lump. If a person scratches this lump, it may break the skin. This can allow bacteria from their hand to enter the bite, leading to an infection.
Infected mosquito bites are common in children and easily treated with antibiotics. It is a good idea to start antibiotics as soon as possible, as soon as you think there may be a bacterial infection.