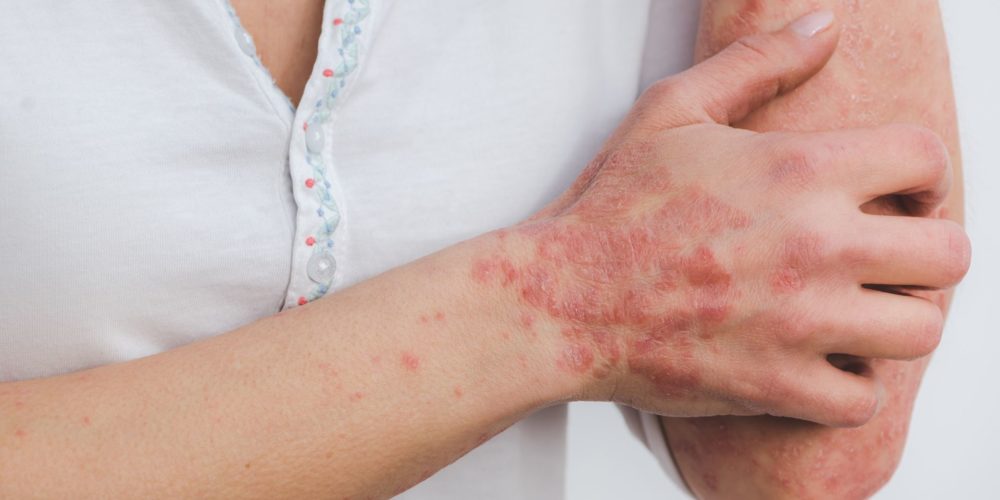
Since no lab tests are usually needed to identify atopic dermatitis (eczema), your doctor will likely make a diagnosis by examining your skin and reviewing your medical history. This means that eczema can be diagnosed and treated via telehealth. Your provider may, however, want to use other tests to rule out other skin diseases.
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It’s common in children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare periodically. It may be accompanied by asthma or hay fever.
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) signs and symptoms vary widely from person to person and include:
- Dry skin
- Itching, which may be severe, especially at night
- Red to brownish-gray patches, especially on hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees, and in infants, the face and scalp
- Small, raised bumps, which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched
- Thickened, cracked, scaly skin
- Raw, sensitive, swollen skin from scratching
Eczema most often begins before age 5 and may persist into adolescence and adulthood. While there is no known cure for atopic dermatitis, some treatments can help to relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks.
Since eczema can be persistent, various treatments over months or years may be needed to control it. And even if treatment is successful, signs and symptoms may return (flare up).
Medications such as creams that control itching and help repair the skin may be prescribed. Some of these creams have side effects, so make sure to speak with your doctor about the side effects of your medication before using.
Antibiotic eczema creams can be prescribed if your skin has a bacterial infection, open sore, or cracks. Oral drugs can be used to control inflammation, although these are only used in short-term treatment, since most can have potential serious side effects.
Therapies such as wet dressings are an effective but intensive treatment for severe atopic dermatitis that involves wrapping the affected area with topical corticosteroids and wet bandages. Ask your doctor about learning how to do this technique at home.
Itchiness is not usually a complaint with a cold, but it is the hallmark of an allergy problem. Coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and other respiratory symptoms. Recurrent red, itchy, dry, sometime scaly rashes in the creases of the skin, wrists, and ankles also may indicate an allergy.

There are a few things you can do to help prevent the severity of eczema.
- Moisturize your skin at least twice a day
- Try to identify and avoid triggers that worsen the condition. Sweat, stress, obesity, soaps, detergents, dust and pollen all could be possible triggers.
- Take shorter baths or showers, and use warm, rather than hot, water.
- Use only gentle soaps
- Dry yourself carefully, and apply moisturizer while your skin is still damp
Dyshidrotic eczema causes small, intensely itchy blisters on the palms of hands, soles of feet and edges of the fingers and toes. While the actual cause of dyshidrotic eczema isn’t known, it’s more common in those who have another form of eczema and tends to run in families.
Many cases of dyshidrotic eczema improve quickly with a short course of topical corticosteroids combined with soaking or applying cool compresses to affected areas a few times a day to help dry out blisters. Dyshidrotic eczema is often linked to a fungal infection, so your dermatologist is likely to prescribe an anti-fungal medication if needed.

At MyCatholicDoctor, we are committed to making Catholic healthcare accessible. Our doctors are committed to care for the whole person – body, mind and spirit. We are pro-life and pro-eternal life.
Thank you for supporting pro-life healthcare.
Please Support Our Pro-life Healthcare
- Pray for MyCatholicDoctor. We invite you to join us at 3 p.m. everyday as we pray the Divine Mercy Chaplet in our own Chapel.
- Choose MyCatholicDoctor for your own healthcare. Do you need labs checked? Need covid Care? We are here to help you.
- Prayerfully consider supporting us financially through a tax deductible donation to our 501(c)(3) not-for-profit foundation. Your donation will directly support providing healthcare.
Our Patrons

Fax: (203) 590-8644
Mailing Address: 1180 Newfield Ave., Stamford, CT 06905
© 2023 MyCatholicDoctor. All rights reserved.
 Notice to California Patients: Medical doctors licensed in California are licensed and regulated by the Medical Board of California. To check up on a license or to file a complaint go to www.mbc.ca.gov, email: [email protected], or call (800) 633-2322. Please also see this notice regarding the Open Payments Database.
Notice to California Patients: Medical doctors licensed in California are licensed and regulated by the Medical Board of California. To check up on a license or to file a complaint go to www.mbc.ca.gov, email: [email protected], or call (800) 633-2322. Please also see this notice regarding the Open Payments Database.